Review of devices used in neuromuscular electrical stimulation for str
Review of devices used in neuromuscular electrical stimulation for str
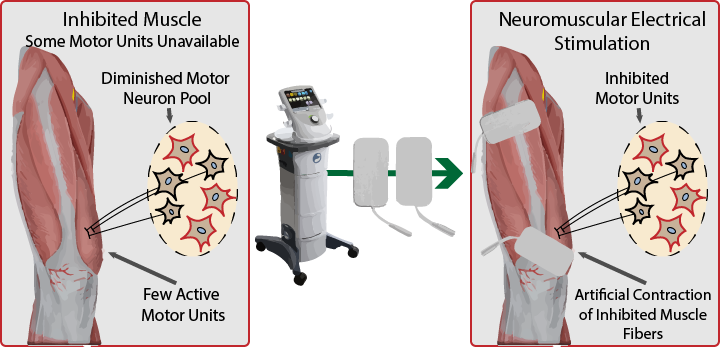
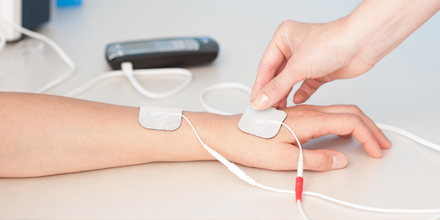
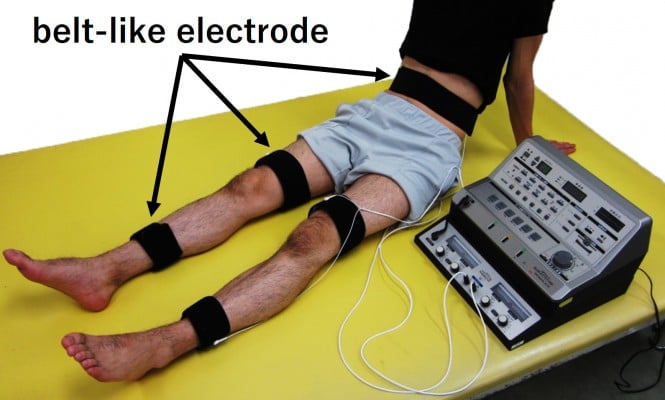
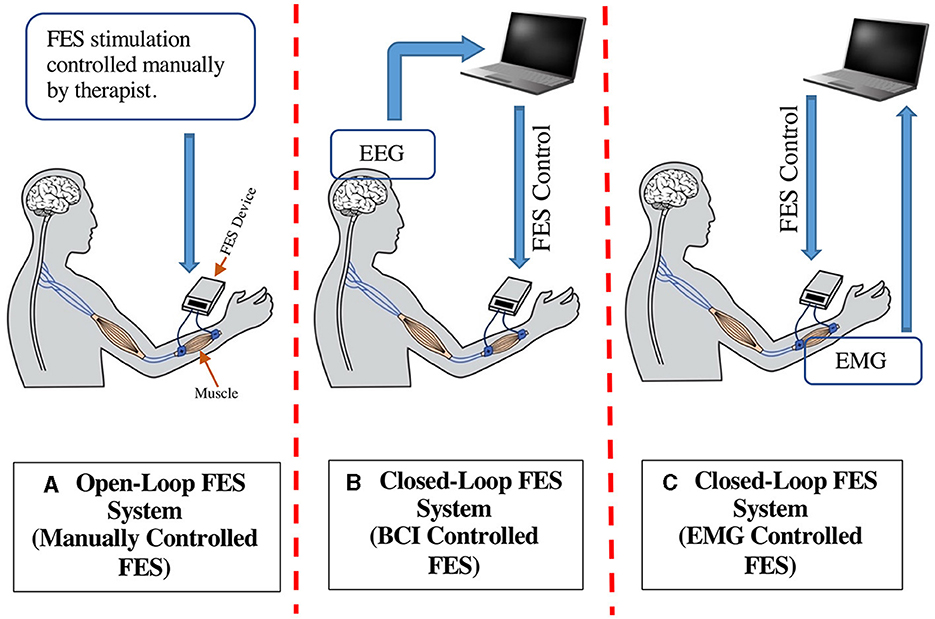
Review of devices used in neuromuscular electrical stimulation for stroke rehabilitation Kotaro Takeda,1 Genichi Tanino,2 Hiroyuki Miyasaka1,3 1Faculty of Rehabilitation, School of Health Sciences, 2Joint Research Support Promotion Facility, Center for Research Promotion and Support, Fujita Health University, Toyoake, Aichi, 3Department of Rehabilitation, Fujita Health University Nanakuri Memorial Hospital, Tsu, Mie, Japan Abstract: Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES), specifically functional electrical stimulation (FES) that compensates for voluntary motion, and therapeutic electrical stimulation (TES) aimed at muscle strengthening and recovery from paralysis are widely used in stroke rehabilitation. The electrical stimulation of muscle contraction should be synchronized with intended motion to restore paralysis. Therefore, NMES devices, which monitor electromyogram (EMG) or electroencephalogram (EEG) changes with motor intention and use them as a trigger, have been developed. Devices that modify the current intensity of NMES, based on EMG or EEG, have also been proposed. Given the diversity in devices and stimulation methods of NMES, the aim of the current review was to introduce some commercial FES and TES devices and application methods, which depend on the condition of the patient with stroke, including the degree of paralysis. Keywords: functional electrical stimulation, therapeutic electrical stimulation, EMG-triggered stimulation, brain–machine interface, brain–computer interface
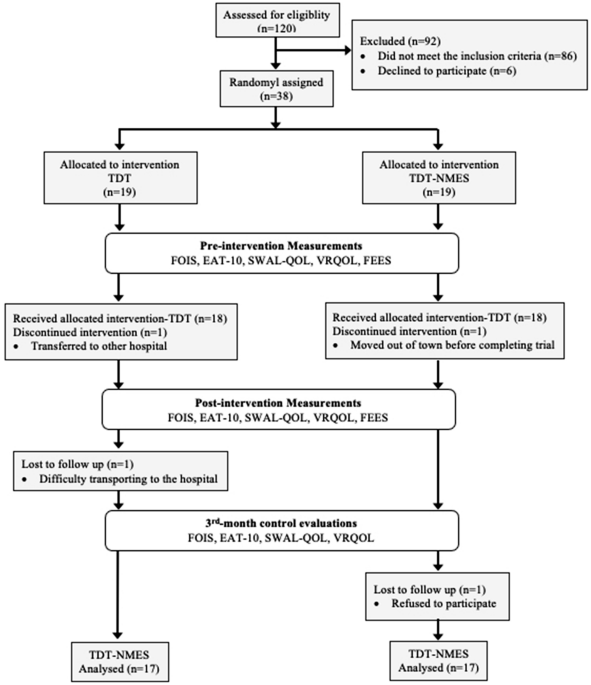
The Effects of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Swallowing Functions in Post-stroke Dysphagia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Functional electrical stimulation therapy for restoration of motor function after spinal cord injury and stroke: a review, BioMedical Engineering OnLine
PDF) Effects of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction on Quadriceps Strength, Function, and Patient-Oriented Outcomes: A Systematic Review
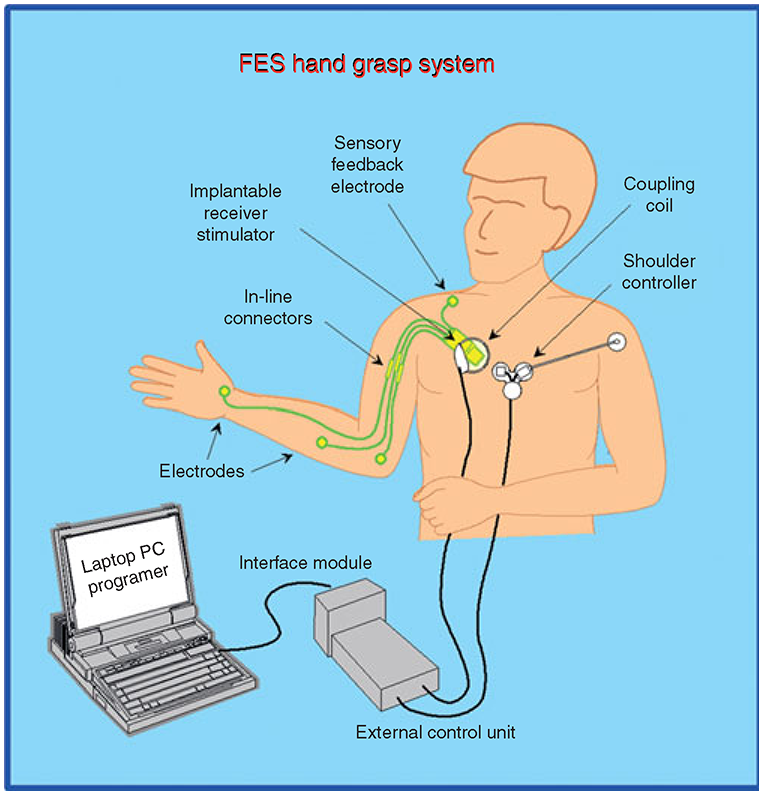
Functional electrical stimulation in neurorehabilitation (Chapter 12) - Textbook of Neural Repair and Rehabilitation
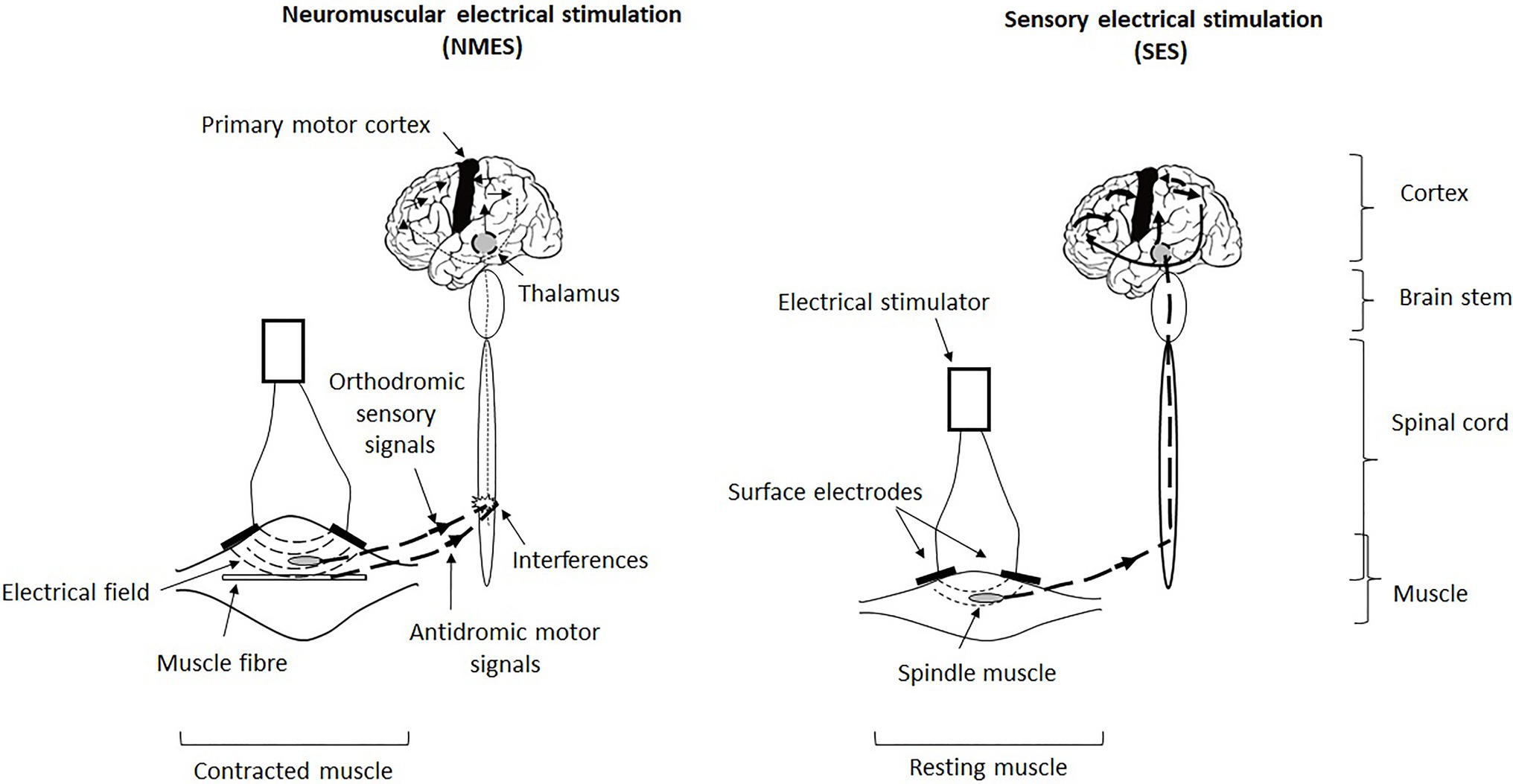
Frontiers Neuromuscular or Sensory Electrical Stimulation for Reconditioning Motor Output and Postural Balance in Older Subjects?

Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Applications - ScienceDirect
Frontiers A systematic review on functional electrical stimulation based rehabilitation systems for upper limb post-stroke recovery

Neuromuscular electrical stimulation for the prevention of venous thromboembolism - Raveena Ravikumar, Katherine J Williams, Adarsh Babber, Hayley M Moore, Tristan RA Lane, Joseph Shalhoub, Alun H Davies, 2018

Effectiveness of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Lower Limbs of Patients With Hemiplegia After Chronic Stroke: A Systematic Review - ScienceDirect
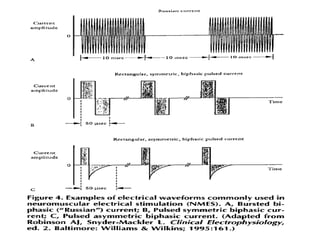
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation

Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation for Motor Restoration in Hemiplegia
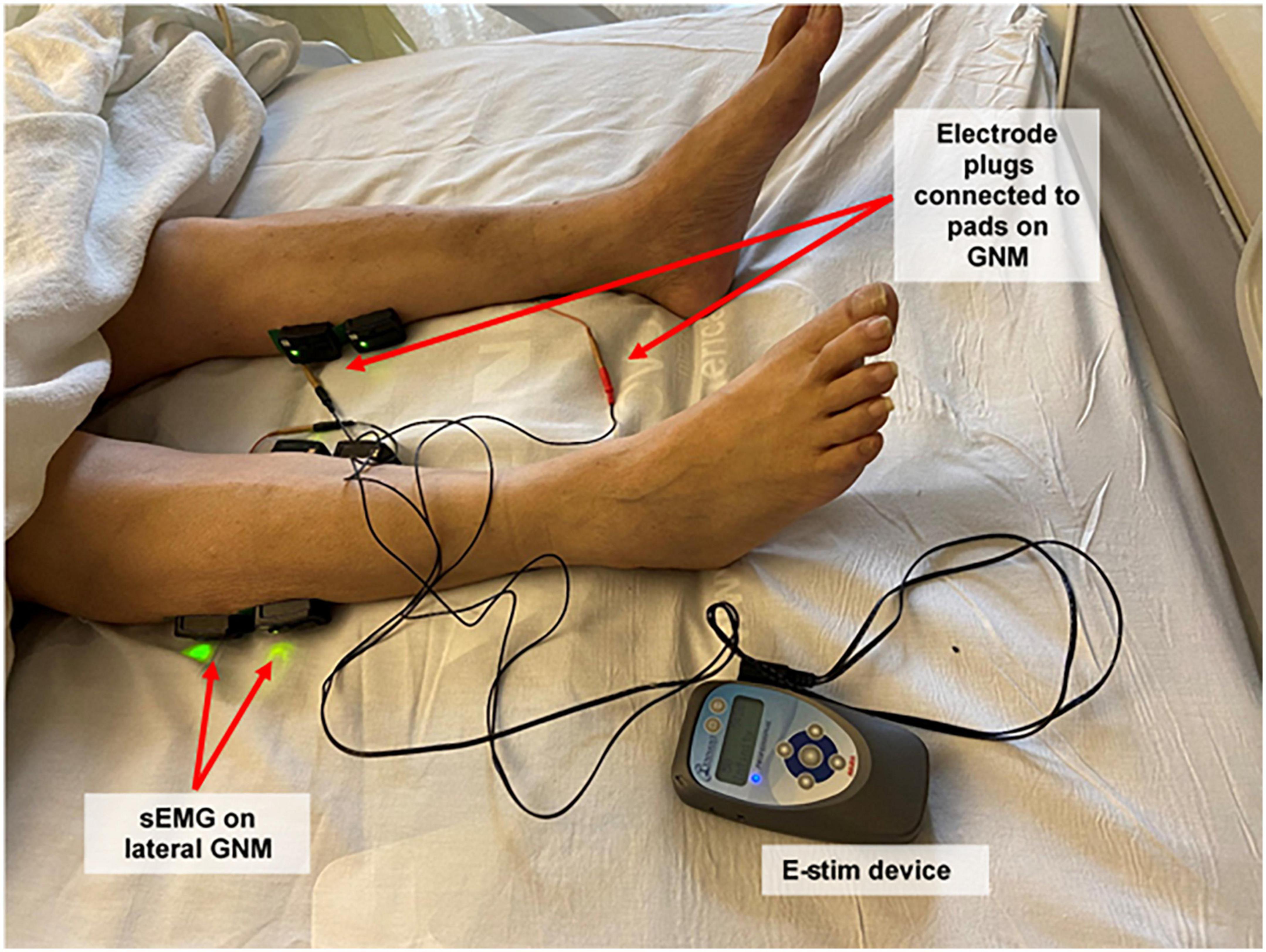
Frontiers Safety and efficacy of electrical stimulation for lower-extremity muscle weakness in intensive care unit 2019 Novel Coronavirus patients: A phase I double-blinded randomized controlled trial